Air conditioners (ACs) are vital to maintaining comfort in homes across the United States, especially during the hot summer months. However, with rising electricity rates and the increasing demand for cooling, it’s crucial to understand how your AC affects your electric bill calculation and overall air conditioning costs.
In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the process of estimating your air conditioner’s annual electricity consumption and how to manage those air conditioning expenses effectively.
Understanding the Basics of AC Energy Consumption
Before we get into the calculations, let’s break down the core components that influence AC energy consumption.
Key Factors Impacting AC Power Consumption
1. Cooling Capacity
The cooling capacity of an air conditioner is typically measured in BTUs (British Thermal Units) per hour. A unit with a higher cooling capacity will consume more energy. Cooling capacity determines how much air an AC can cool per hour, which directly impacts annual energy usage.
2. AC Energy Efficiency
The energy efficiency of your air conditioning unit is measured by its SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) or EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio). A higher SEER rating means that the AC uses less energy to cool a given amount of space, thus reducing electric power consumption.
3. Usage Patterns
How long your AC runs each day, how often it cycles, and how many days it’s in operation all play a crucial role in determining electricity consumption and, ultimately, cooling costs. This varies based on climate, time of year, and the insulation of your home.
4. Electricity Rates in the USA
Electricity rates in the United States can vary significantly by region. These kilowatt-hour rates (kWh) affect your monthly AC usage cost. For example, California electricity rates can be much higher than those in Texas, directly impacting your air conditioner operating costs.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculate Your Annual Air Conditioning Bill
Understanding the formula for calculating air conditioning running costs is vital for homeowners. Let’s break down the calculating annual AC energy consumption process:
Step 1: Determine the Cooling Capacity and SEER Rating
- Cooling Capacity (BTU/h): This refers to how much heat the air conditioner can remove from the air per hour. A higher BTU means more cooling power, but also higher electric power consumption.
- SEER Rating: This is the efficiency rating of your AC. For example, a SEER 14 unit uses less energy than a SEER 8 unit for the same cooling load.
Step 2: Estimate Daily Operating Hours
Estimate how many hours your air conditioner operates each day. In most households, air conditioners run for about 6-12 hours per day, depending on the weather and home insulation.
Step 3: Calculate Energy Consumption Per Day
You can calculate the electricity consumption per hour using the formula:

Step 4: Calculate Annual Energy Usage
Multiply your daily energy consumption by the number of days the AC runs annually. For example, if your AC runs for 120 days during the summer:
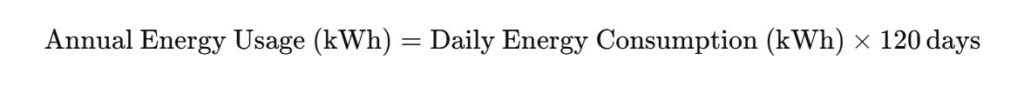
Step 5: Estimate Your Annual Cost
Multiply the annual energy usage by your local electricity rates USA:
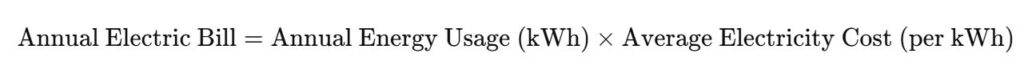
This will give you an energy bill estimation for the entire year.
Example Calculation of Annual Air Conditioner Costs
Let’s walk through an example calculation for a 12,000 BTU air conditioner with a SEER rating of 14. The electricity rate in this example is 0.15 USD per kWh.
- Cooling Capacity: 12,000 BTU/h
- SEER Rating: 14
- Operating Hours per Day: 8 hours
- Operating Days per Year: 120 days
- Electricity Rate: 0.15 USD per kWh
Daily Energy Consumption
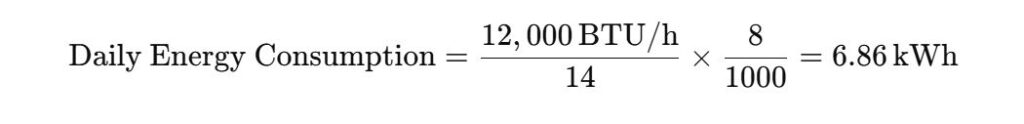
Annual Energy Usage
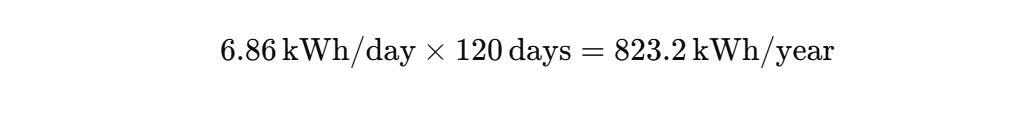
Annual Electric Bill
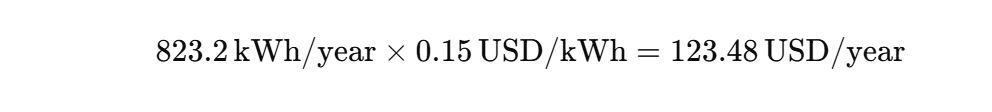
How Electricity Rates Impact AC Costs
The electricity rates USA vary greatly across different states. Understanding these kilowatt-hour rates is crucial for estimating air conditioning expenses accurately.
| State | Average kWh Rate (USD) |
|---|---|
| Hawaii | 0.42 |
| California | 0.31 |
| Texas | 0.11 |
| Florida | 0.12 |
| Washington | 0.09 |
In states like Hawaii, air conditioning costs can be significantly higher due to elevated electricity rates, while states like Washington offer relatively lower costs.
Tips for Reducing Air Conditioning Energy Costs
By improving AC energy efficiency and following energy-saving tips, you can lower your summer electricity bill and keep cooling costs under control.
1. Upgrade to Energy-Efficient Air Conditioners
Switching to energy-efficient air conditioners with higher SEER ratings can reduce energy consumption in summer. Energy-efficient air conditioners use less power to cool your home, lowering air conditioning running costs.
2. Optimize Thermostat Settings
A simple way to cut costs is by setting your thermostat to 78°F (25.5°C) when you are at home and increasing the temperature when you are away. Each degree above 78°F can save you 3% on your home energy bills.
3. Regular Maintenance
Regularly cleaning your AC’s filters and checking the refrigerant levels helps maintain air conditioner efficiency, which directly impacts HVAC electricity consumption.
4. Insulate Your Home
Proper insulation reduces the amount of heat entering your home, which means your AC doesn’t have to work as hard. This improves cooling system efficiency and reduces overall residential cooling costs.
5. Use Ceiling Fans
Using ceiling fans along with your air conditioner can improve cooling system efficiency, allowing you to raise the thermostat temperature by a few degrees without sacrificing comfort.
The Role of AC in Summer Electricity Bills
Air conditioning is one of the most significant contributors to summer electricity bills. Understanding how your AC operates and its annual energy usage allows you to make informed decisions about optimizing your air conditioner operating costs.
Conclusion
Calculating your air conditioner’s annual electricity bill and understanding the factors that affect your air conditioning costs is crucial for managing home energy bills. By following the steps outlined in this guide and implementing energy-saving tips, you can significantly reduce your cooling costs and achieve a more efficient, cost-effective air conditioning system.
Remember, investing in energy-efficient air conditioners and upgrading your home’s insulation can yield long-term savings, making it easier to enjoy comfort without the hefty price tag. Stay mindful of your HVAC costs, and with regular maintenance, you can keep your electric bill calculation under control each year.



